Europe’s rich array of biodiversity, habitats and species are under threat due to human activities and climate change. This degradation affects our well-being and economy. The EU is taking action to restore and protect the vital systems that support life on our planet.
The European continent is home to a wealth of habitats and species — both land-based and marine. Centuries of human activities, however, have taken a toll on Europe’s biodiversity. Our nature has been transformed and heavily impacted, with most of Europe’s species and habitats facing an uncertain future unless urgent and more ambitious action is taken.
Despite some progress, most protected habitats and species have either poor or bad conservation status. Destruction of habitats, overexploitation of resources, pollution, climate change, the introduction of invasive species, urban sprawl and landscape fragmentation are only some of the reasons behind this decline, which affects terrestrial and aquatic species, their habitats and ecosystem services.
The good news is that there are signs of recovery in some areas thanks to ongoing efforts to reduce certain impacts, such as those caused by contaminants, eutrophication and overfishing in marine ecosystems.
Awareness of the importance of biodiversity is also growing and many initiatives and policies are already in motion. Both the number and area of protected sites under the EU’s Natura 2000 network have increased. With new policy proposals like the EU Restoration Law, Europe wants to strengthen its efforts not only to preserve and protect but also to restore Europe’s nature.
Europe’s nature under pressure
Europe’s biodiversity continues to decline at an alarming rate, with most protected species and habitats confronting poor conservation status. Much more effort is needed to reverse current trends and to ensure resilient and healthy nature.
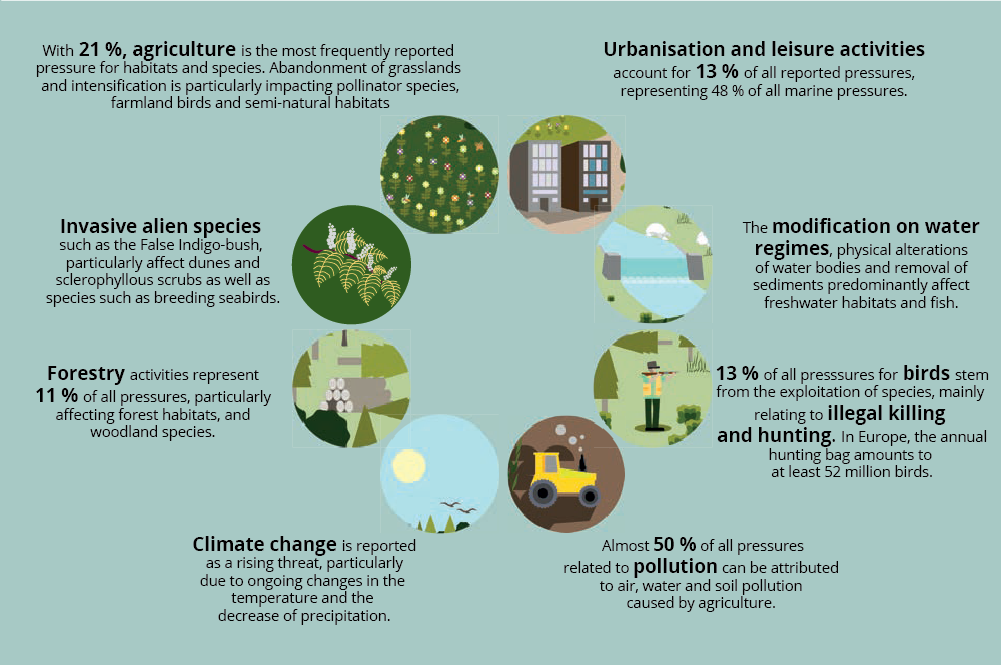
The pressures on biodiversity may vary depending on the habitat, region or species. Our assessments show that many agricultural activities, intensifying land management practices, and the abandonment of extensive management are the most common overall pressures.
Urbanisation and leisure activities are the second largest pressure and it particularly affects habitats such as dunes and coastal and rocky habitats. Forestry activities are the main source of pressure on arthropods, mammals and non-vascular plants. The pollution of air, water and soil from agriculture in particular, affects most habitats, especially in the European Union’s Atlantic and continental regions.
What causes biodiversity loss in Europe?
How does pollution impact ecosystems?
One of the major drivers of biodiversity loss and decline in Europe and worldwide is pollution. Pollution puts pressure on freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems, the functions they maintain and the services they provide.
The types of pollutants that affect ecosystems are wide-ranging — from human-made chemical products, nutrients (e.g. nitrogen) and microplastics to ambient sources such as noise and light.
One of the sections of our zero pollution monitoring assessment examines available knowledge and trends in pollution and associated impacts on ecosystems.
Global biodiversity protection requires global action
At the UN Biodiversity conference COP15 in Montréal, Canada, the EU joined 195 countries in the historic Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. This framework contains global goals and targets aiming to protect and restore nature for current and future generations, ensure its sustainable use as well as spur investments for a green global economy. Together with the Paris Agreement on climate, it paves the way towards a climate-neutral, nature-positive and resilient world by 2050.
The European Union is a leading player in global biodiversity efforts and negotiations, including COP15.




